The automotive industry has undergone significant transformations over the past century. From the first gas-powered vehicles to the modern-day electric and hybrid cars, the evolution of automobiles has been driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and consumer demand. Buyers are faced with a choice – hybrid vs. electric vs. gas vehicles. In this blog, I’ll help you make an informed decision on which car type is the best choice for your lifestyle and driving preferences.
Overview of Car Types
When it comes to choosing a car, there’s a lot to think about, and the type of engine under the hood is probably one of the most important decisions you’ll make. Over the years, I’ve explored the ins and outs of gasoline, hybrid, and electric cars, and each has its own charm (and quirks).
Whether you’re drawn to the nostalgia of a roaring gas engine, the eco-friendly appeal of hybrids, or the cutting-edge technology of electric vehicles, understanding how these car types work is the first step to finding the right fit. Let’s break them down!
Gasoline Cars
Gasoline cars, also known as internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, rely entirely on a gas-powered engine to generate power. This engine burns fuel to produce energy, which is then used to drive the wheels. Gas-powered cars have been the cornerstone of the automotive industry since their inception in the late 19th century, dominating roads for over a century due to their reliability and widespread adoption.
Gasoline cars revolutionized transportation by providing an efficient, convenient means of travel compared to horse-drawn carriages. Brands like Ford, General Motors, and Toyota built their legacies on ICE technology, creating iconic models that remain popular today.
| Pros | Cons |
| Widely available refueling infrastructure | High greenhouse gas emissions |
| Proven performance and long-range capabilities | Higher maintenance costs due to complex engines |
| Generally lower upfront costs compared to hybrids and EVs | Dependency on fluctuating oil prices |
Hybrid Cars
Hybrid cars combine a traditional gas engine with an electric motor and battery, allowing for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. They operate by switching between or blending the two power sources, optimizing performance for different driving conditions. Types of hybrids include the following:
- Mild hybrids – Use a small electric motor to assist the gas engine but cannot run solely on electric power.
- Full hybrids – Capable of running on electric power alone for short distances or in combination with the gas engine.
- Plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) – Feature larger batteries that can be charged via an external source, offering extended electric-only driving range.
| Pros | Cons |
| Better fuel economy compared to gas cars | Higher upfront costs |
| Lower emissions, particularly in urban driving conditions | Still rely on fossil fuels to some extent |
| Versatility in driving modes | More complex systems may increase maintenance costs over time |
Electric Cars (EVs)
Electric vehicles (EVs) are powered entirely by an electric motor, which draws energy from a rechargeable battery pack. Unlike gas or hybrid cars, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them a leading choice for eco-conscious drivers. Types of EVs include the following:
- Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) – Fully electric, relying entirely on battery power for operation. Examples include the Tesla Model 3 and Nissan Leaf.
- Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) – Combine a battery-powered motor with a gas engine, offering the option to switch between electric and hybrid modes.
| Pros | Cons |
| Zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing environmental impact | Higher initial purchase price |
| Lower maintenance requirements (no oil changes or exhaust systems) | Limited driving range compared to gas vehicles, though improving with technology |
| Innovative features and advanced technology integration | Charging infrastructure is still developing in many areas |
Comparative Analysis of Hybrid vs. Electric vs. Gas
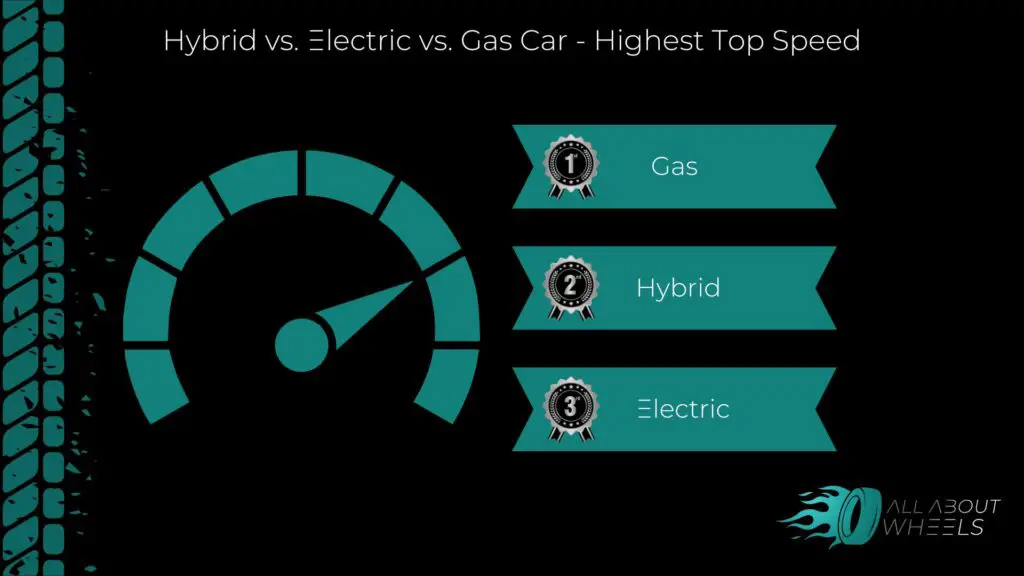
Let’s start with the performance of each of these types of cars. Gas cars are known for their proven power, especially in high-performance and sports car models. Gas engines provide consistent and reliable acceleration.
On the other hand, hybrids offer balanced performance, ideal for daily driving. They can switch seamlessly between gas and electric power, optimizing efficiency. When it comes to EVs, they deliver instant torque, resulting in smooth and quick acceleration. Electric motors provide a unique, responsive driving experience.
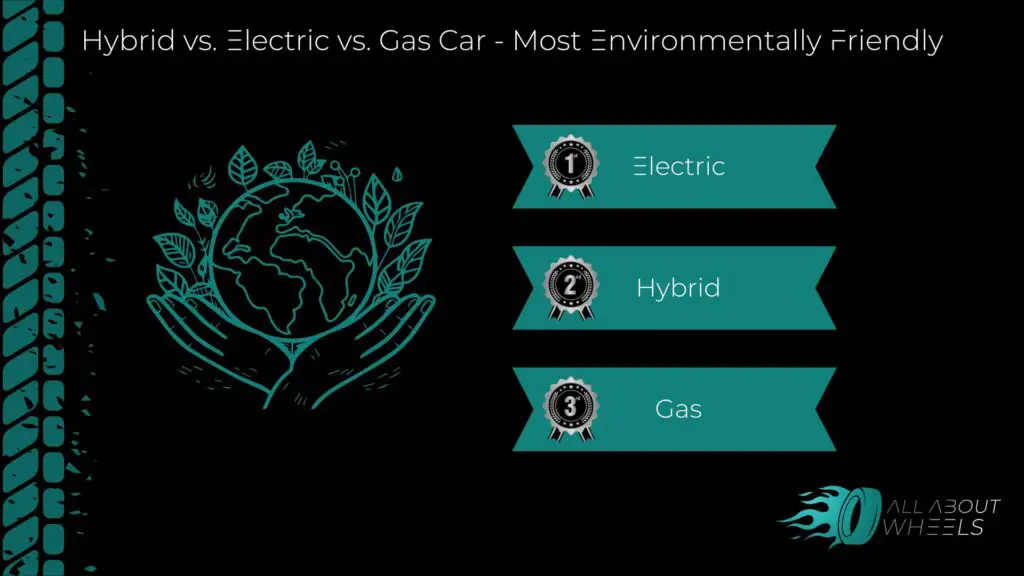
Environmental Impact
Gas vehicles have the highest emissions among the three, contributing significantly to air pollution and climate change. Hybrids emit less CO2 than gas cars due to their partial reliance on electric power but still depend on fossil fuels. Finally, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them the most eco-friendly option. However, environmental concerns remain around the extraction of raw materials for batteries and the recycling process.
Cost of Ownership
When considering the cost of ownership, each type of vehicle – gas, hybrid, and electric – offers a different financial picture. Here’s the cost of ownership information in the table below:
| Aspect | Gas cars | Hybrids | EVs |
| Upfront costs | Typically the cheapest to purchase upfront. | Falls in the mid-range for initial cost. | Tend to have the highest initial price due to advanced battery technology. |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent maintenance (oil changes, engine repairs). | Involves moderate maintenance due to dual power systems. | Minimal maintenance needs due to fewer moving parts. |
| Fuel/energy costs | Gas prices fluctuate, leading to unpredictable refueling costs. | Saves on fuel compared to gas cars. | Cheapest to “refuel,” as electricity is generally less expensive than gasoline. |
Range and Convenience
When it comes to range and convenience, gas cars lead the pack with the longest range on a single tank and the advantage of widespread refueling infrastructure. Hybrids offer a solid middle ground, providing a decent range and requiring less frequent refueling than gas cars. EVs, while improving in range thanks to advancements in battery technology, are still limited by the availability of charging stations and longer charging times compared to the quick refueling of gas cars.
Driving Experience
The driving experience varies significantly between car types. Gas cars offer a traditional feel, complete with the roar of the engine, a feature many enthusiasts find appealing. Hybrids provide a similar experience but operate more quietly thanks to their electric motor. EVs stand out with their silent operation and advanced technology features, such as regenerative braking and, in some models, autonomous driving capabilities, delivering a modern and futuristic driving experience.
Key Use Cases and Recommendations
Choosing the right car depends on how and where you plan to use it. Whether you’re navigating city streets, embarking on long road trips, indulging in your passion for cars, or striving to reduce your environmental footprint, each vehicle type has distinct advantages. Below, we break down the key use cases and provide recommendations to help you find the perfect fit.
City Driving
For urban dwellers, hybrids and EVs are excellent choices. Both offer lower emissions and better efficiency, especially in stop-and-go traffic. EVs, in particular, excel in cities with robust charging infrastructure, while hybrids provide the flexibility of gas for occasional longer trips.
Long-Distance Travel
Gas cars remain the go-to option for extended road trips, thanks to their long range and the abundance of refueling stations. Some hybrids also perform well for long-distance travel, combining improved fuel efficiency with the convenience of a gas engine.
Enthusiasts and Hobbyists
For car enthusiasts and hobbyists, gas-powered vehicles hold a timeless appeal. From the growl of a classic muscle car to the high-performance capabilities of sports cars, gas cars deliver a driving experience that resonates with those who value tradition and power.
Eco-Conscious Drivers
If minimizing environmental impact is your priority, EVs are the clear winner. With zero tailpipe emissions and increasing availability of renewable energy for charging, electric vehicles are the most eco-friendly option on the market. While hybrids also reduce emissions, they can’t match the green credentials of a fully electric vehicle.
Recent Market Statistics
Understanding current market trends is essential when evaluating the future of gas, hybrid, and electric vehicles. Here are some recent statistics that highlight the evolving automotive landscape:
- Electric vehicles (EVs) – In 2023, global sales of electric cars reached approximately 14 million units, marking a 35% increase from 2022. This surge brought the total number of electric cars on the road to 40 million, indicating robust growth in the EV sector.
- Hybrid vehicles – In the United States, hybrid vehicle sales have experienced significant growth. In 2023, Americans purchased 53% more hybrid cars compared to 2022, reflecting a strong consumer interest in fuel-efficient alternatives.
- Market share in the US – By the third quarter of 2024, electric and hybrid vehicles combined accounted for 21.2% of total new light-duty vehicle sales in the United States. Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) alone made up 8.9% of the market, while hybrid vehicles reached a record 10.6% share, underscoring the increasing adoption of alternative fuel vehicles.
- Global EV sales growth – The global market for electric vehicles continues to expand rapidly. In 2023, a total of 14.2 million new battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) were delivered worldwide, representing a 35% increase from the previous year.
These statistics illustrate a clear shift in consumer preferences toward more sustainable vehicle options, with both hybrid and electric vehicles gaining substantial market share globally and in the United States.
Future Trends and Considerations
The automotive industry is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting regulations. These changes will shape the future of transportation, offering both opportunities and challenges for car enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike.
Advancements in EV Technology
Electric vehicles are at the forefront of innovation, with significant improvements on the horizon. Developments in solid-state batteries promise faster charging times, enhanced safety, and extended range. Additionally, increasing investments in EV infrastructure and renewable energy integration will make owning an electric car more practical and appealing.
Decline of Gas Cars
Gas-powered vehicles are facing a steady decline as governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations and incentivize greener alternatives. Consumer preferences are also shifting toward more sustainable options, further pushing traditional gas cars out of favor.
Potential Hybrid Dominance
During the transition to a fully electric future, hybrids are poised to dominate. They offer a practical compromise by combining the familiarity of gas engines with the efficiency of electric motors, making them a popular choice for drivers not ready to commit to an all-electric vehicle. Hybrid technology continues to evolve, bridging the gap between traditional and electric cars.

Making the Right Choice
Choosing between gas, hybrid, and electric cars ultimately depends on your unique needs, lifestyle, and priorities. Gas cars remain a reliable and affordable option with extensive refueling infrastructure, making them ideal for long-distance travel or traditional driving experiences. Hybrids strike a balance between better fuel efficiency and lower emissions, suitable for those seeking versatility.
Meanwhile, EVs stand out as the eco-friendliest choice, offering innovative technology and minimal maintenance, despite higher upfront costs and infrastructure challenges. Each vehicle type has its own strengths and limitations, and the right choice depends on what matters most to you – be it cost, performance, environmental impact, or convenience.








